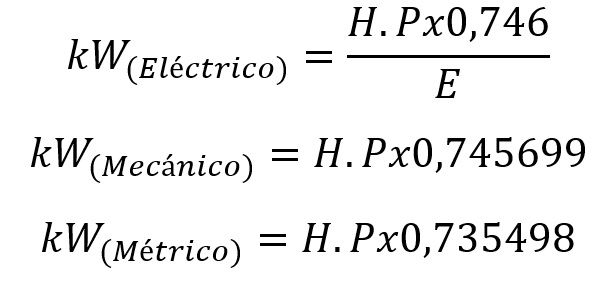Conversion from hp to kW is simply calculated. This article explains essential formulas and guides through practical engineering examples properly.
Discover clear calculation processes, critical conversion techniques, and real-life cases. Keep reading to master horsepower to kilowatt conversions confidently accurately.
AI-powered calculator for Conversion from hp to kW
Example Prompts
- “Find kW for 50 hp”
- “Convert 150 hp to kW”
- “Calculate the kW value for 75 hp”
- “Determine the kilowatt equivalent for 300 hp”
Understanding the Units: Horsepower and Kilowatt
Horsepower (hp) and kilowatt (kW) are widely used in various industries, including automotive, manufacturing, and energy sectors. Understanding their differences is crucial when comparing engines and machinery.
Horsepower was originally developed to compare the output power of steam engines with draft horses. It has several definitions including mechanical, metric, and electrical HP, which vary slightly in value. Commonly used mechanical horsepower is defined as 1 hp = 745.7 watts, while metric horsepower is approximately equal to 735.5 watts.
Kilowatt is a unit constructed under the SI system. One kilowatt equals 1,000 watts, providing a simple metric unit for power calculations in scientific and engineering contexts.
Conversion Factors and Basic Formulas
To convert from horsepower to kilowatt, the following fundamental formula is used:
Power in kW = Power in hp × Conversion Factor
In this formula, the “Conversion Factor” is dependent on the type of horsepower used:
- kW: Kilowatts or 1000Watts
- Hp: Horsepower or horse power
- E: Motor efficiency.
For most technical applications, especially those related to electrical engineering, mechanical horsepower is assumed, unless stated otherwise.
Using the mechanical horsepower conversion factor, the formula simplifies to:
Power in kW = Power in hp × 0.7457
Each variable in the formula is defined as follows:
- Power in hp: The horsepower rating of the engine or device.
- 0.7457: The conversion factor for converting mechanical horsepower to kilowatts, based on the equivalence 1 hp = 745.7 watts.
- Power in kW: The resulting power measured in kilowatts after conversion.
Additional Conversion Formulas
For cases involving metric horsepower, the conversion formula is slightly different:
Power in kW = Power in hp × 0.7355
The variables remain consistent with the previous explanation, except that the conversion factor is adjusted according to the metric hp definition. It is important to confirm which horsepower standard is referenced before performing any calculations.
Extensive Conversion Tables
Below are detailed tables for converting horsepower to kilowatts using both conversion factors. These tables provide a quick reference for various power ratings and are optimized for clarity on WordPress sites.
Conversion Table for Mechanical (Imperial) Horsepower to kW
| Horsepower (hp) | Power (kW) |
|---|---|
| 1 hp | 0.7457 kW |
| 5 hp | 3.7285 kW |
| 10 hp | 7.457 kW |
| 25 hp | 18.6425 kW |
| 50 hp | 37.285 kW |
| 100 hp | 74.57 kW |
| 200 hp | 149.14 kW |
Conversion Table for Metric Horsepower to kW
| Horsepower (hp) | Power (kW) |
|---|---|
| 1 hp | 0.7355 kW |
| 5 hp | 3.6775 kW |
| 10 hp | 7.355 kW |
| 25 hp | 18.3875 kW |
| 50 hp | 36.775 kW |
| 100 hp | 73.55 kW |
| 200 hp | 147.10 kW |
HP to kW Conversion Table: Equivalence and Transformation
Equivalence of HP to kW for Three-Phase Motors
| How many HP are?: | Equivalence in kW |
| 1/8 1/6 1/4 1/3 1/2 3/4 1 1.5 2 3 4 5 5.5 7.5 10 12.5 13.5 15 20 25 30 40 50 60 75 100 125 150 175 200 | Equivalence to 0.1 kW 0.12 kW 0.18 kW 0.25 kW 0.37 kW 0.56 kW 0.75 kW 1.1 kW 1.5 kW 2.2 kW 3.0 kW 3.7 kW 4.0 kW 5.5 kW 7.5 kW 9.3 kW 10 kW 11 kW 15 kW 18 kW 22 kW 30 kW 37 kW 45 kW 55 kW 75 kW 90 kW 110 kW 130 kW 150 kW |
Equivalence of Hp to kW for single-phase motors:
| How many Hp are: | Equivalence en kW |
| 1/12 1/8 1/6 1/4 1/3 1/2 3/4 1 | Equivalence to 0.07 kW 0.1 kW 0.12 kW 0.18 kW 0.25 kW 0.37 kW 0.56 kW 0.75 kW |
| 1.5 2 3 4 5 5.5 7.5 10 | 1.1 kW 1.5 kW 2.2 kW 3 kW 3.7 kW 4 kW 5.5 kW 7.5 kW |
The tables are based on engines of approximately 1450rpm efficiency and average power factor.
Wide variations of these tables can arise, especially in single-phase motors, therefore engineers should, whenever possible, check the motor nameplate in each case.
Practical Considerations in Engineering Applications
Engineers and technicians often encounter scenarios where equipment ratings are given in horsepower. In contrast, design calculations and simulations use kilowatts. For example, when determining the load capacity of an electric motor in an industrial setup, precise conversion is needed.
Moreover, regulatory documents and best practice guidelines usually adhere to SI units, making the conversion from hp to kW essential for compliance with local and international standards. These standards ensure compatibility and consistency across different components of an electrical system.
Real-World Example 1: Conversion in an Industrial Motor Application
Consider an industrial facility that uses a motor rated at 100 horsepower. The facility’s electrical design requires power input in kilowatts. Using the mechanical horsepower conversion factor, the engineer calculates the motor’s power in kilowatts as shown:
Power in kW = 100 hp × 0.7457 = 74.57 kW
The engineer then uses this value to design an electrical system capable of handling the motor’s load. Detailed steps include:
- Reviewing manufacturer data sheets to confirm the theoretical horsepower rating.
- Multiplying the horsepower by the conversion factor to obtain the kilowatt value.
- Designing protective circuitry (circuit breakers, relays) based on the converted power value to ensure electrical safety.
- Calculating the energy consumption over time factoring in the gearing efficiency, ambient conditions, and load variations.
In this scenario, the conversion is critical for ensuring that the facility’s power distribution network is appropriately sized and meets safety standards. The accurate conversion from hp to kW serves as a foundation for designing energy-efficient systems that align with both national and international engineering practices.
Real-World Example 2: Application in HVAC System Design
HVAC systems in large commercial buildings often include motors rated in horsepower. Suppose an HVAC system uses a compressor with a rating of 50 horsepower. The engineer is tasked with determining the appropriate generator capacity in kilowatts.
Applying the conversion for mechanical horsepower, the calculation is as follows:
Power in kW = 50 hp × 0.7457 = 37.285 kW
In the design process, the engineer considers the following steps:
- Verify the compressor’s total load requirements and the impact of starting currents, which may exceed the nominal running power.
- Convert the horsepower rating to kilowatts to integrate with other SI unit-based calculations within the system design software.
- Design the backup generator system to accommodate peak loads that occur during startup, often incorporating a safety margin (typically 10-20% above the calculated kW value).
- Consult local fire and building safety codes that require precise power conversion metrics for substations and emergency systems.
Using careful conversion and integrating industry standards enhances system reliability while ensuring that the HVAC system’s power requirements are accurately met. This real-world example illustrates the necessity for precise engineering calculations in the design and maintenance of complex systems.
Additional Considerations and Best Practices
When conducting conversions from horsepower to kilowatt, it is essential to adhere to certain best practices. These include cross-checking values with manufacturer specifications, using updated conversion factors, and validating the results with simulation software.
Engineers should maintain a repository of references, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) and guidelines from professional bodies like IEEE and IEC, to ensure that all conversions and design decisions are based on current engineering standards.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
One common mistake is confusing the type of horsepower in use. Always ensure whether the horsepower is mechanical, metric, or electrical before beginning a conversion procedure. Misinterpretation can lead to significant errors in power calculations.
Another pitfall is rounding off too early in the calculation process. Retaining precision throughout the conversion process minimizes cumulative errors. It is advisable to perform multiplications with all decimal digits and round the final result when necessary.
Technical Tips for Accurate Conversions
Always verify the units provided in technical documents. If a device specification lists power in hp, look for accompanying information on the measurement type.
Utilize engineering calculators, simulation tools, or custom-built Excel sheets that incorporate unit conversion functions to eliminate manual errors. When in doubt, consult authoritative sources such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) guidelines for additional verification.
Industry Standards and Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory compliance often necessitates accurate unit conversions in technical documentation and safety certifications. For example, industrial motor installations must adhere to IEC standards, which standardize power and energy calculations across different equipment types.
By ensuring that horsepower ratings are converted accurately to kilowatts, engineers comply with both national and international standards, thereby preventing misapplication of equipment and ensuring efficient energy management.